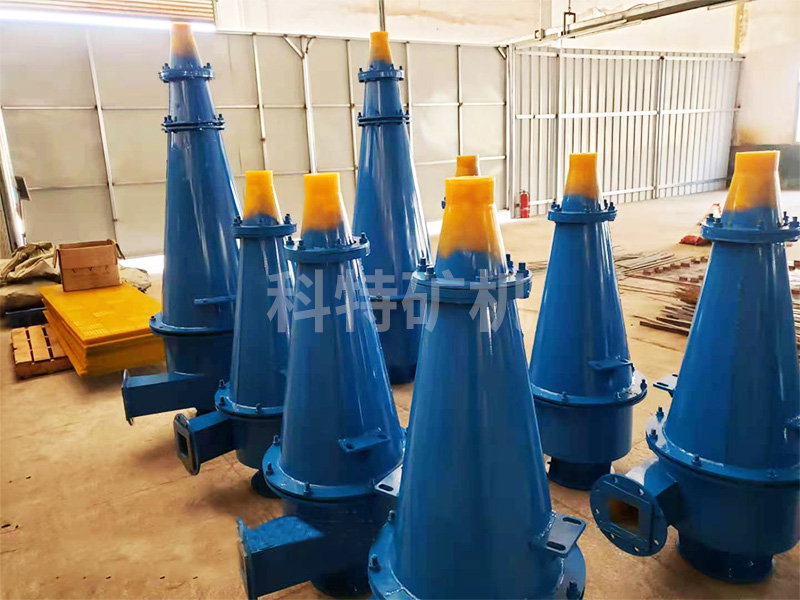

Hydrocyclone
- 60s quick Q & A
- 30min reply
- 24h free program

Product introduction:
Hydrocyclone is an equipment used to separate and remove heavy coarse-grained mud and sand in sewage. Sometimes it is also used for mud dewatering.
It is divided into pressure type and gravity type. It is often made of circular cylindrical structures or metal pipes. Water enters from the upper part of the structure (or metal pipe) along the tangent line by pressure or gravity. Under the action of centrifugal force, coarse particulate matter is thrown to the wall and rotated downward to discharge together with the formed concentrated liquid. Smaller particles rotate to a certain extent and are discharged with the secondary uprotation vortex.

Basic form:
In normal production hydrocyclones, the movement forms of fluid are divided into the following types.
1. Outer swirl and inner swirl
Outer swirl and inner swirl are the main forms of motion of hydrocyclone. Their rotation direction is the same, but their motion direction is opposite. The coarse and heavy solid material carried by the external cyclone is discharged from the grit chamber and is the grit product; The inner swirl carries fine and light solid materials, which are discharged from the overflow port, which is overflow. See the figure for details
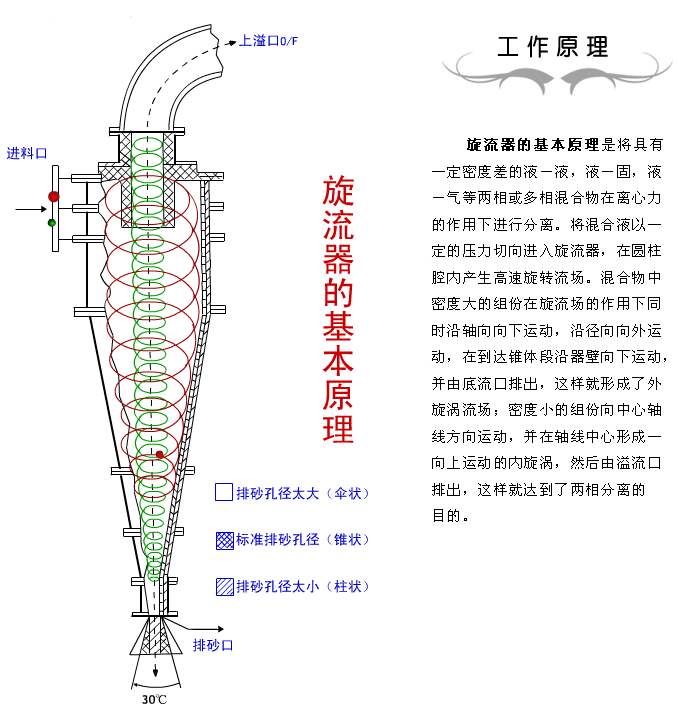
2. Short circuit current
Due to the friction resistance of the cyclone wall, part of the two-phase fluid fed into the cyclone moves upward first, then inward along the lower surface of the top cover, and then downward along the outer wall of the vortex overflow pipe. Finally, it converges with the inner vortex and is discharged from the overflow port of the overflow pipe. This part of under cover flow is commonly referred to as short-circuit flow. Because it directly enters the overflow product without separation, it directly affects the separation effect.
3. Circulating flow
For the two-phase fluid that moves inward from the outer vortex to the inner vortex in the form of spiral vortex, because the overflow port of the overflow pipe is too late to discharge it all, part of the fluid that has not been discharged will circulate from bottom to top and then from top to bottom in the space between the vortex overflow pipe of the hydrocyclone and the wall of the hydrocyclone to form a circulating flow.
4. Zero velocity envelope
Because the fluid motion modes of outer swirl and inner swirl are different, and the inner swirl is formed by the gradual inward migration during the movement of outer swirl, there must be a trace point in which the axial velocity is equal to zero. In the normal separation process of hydrocyclone, the track with zero axial velocity of fluid is called zero velocity envelope. The zero velocity envelope is not only the center line of the circulating flow, but also the boundary between the inner swirl and the outer swirl. The shape and size of the zero velocity envelope of the hydrocyclone with certain structural parameters are basically unchanged.
Maximum tangent velocity trajectory surface
When the two-phase fluid fed into the cyclone moves inward in the form of spiral vortex, the tangent velocity of the fluid particle has a maximum value, that is, the maximum tangent velocity. During normal operation, the trajectory of maximum tangential velocity of fluid particles in the hydrocyclone is called maximum tangential velocity trajectory surface.

5. Air column
When the two-phase fluid fed into the hydrocyclone moves as a spiral vortex, with the gradual reduction of the rotation radius, the particle tangent velocity becomes larger and larger. When it reaches a certain value, a negative pressure zone lower than the external space pressure will be formed. The fluid entering the negative pressure area will precipitate air from it. At the same time, the air in the external space will also enter the negative pressure area through the discharge outlet (grit chamber and overflow port) to form an air column.
- Prev:Spiral classifier
- All
- Next:Dewatering screen

